Dynamic
Certificate
Pinning
Dynamic Certificate Pinning
Dynamic Certificate Pinning is a technique used to enhance the security of a mobile app by ensuring that it only communicates with a trusted server whose digital certificate matches a predefined set of certificates. It protects the app against Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attacks. Dynamic updates allow the app to handle changes certificates without requiring a code update.
Benefits
Protect your customer data and prevent reverse engineering of app traffic
Block all Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attacks
Change pins as needed and dynamically update all your apps immediately
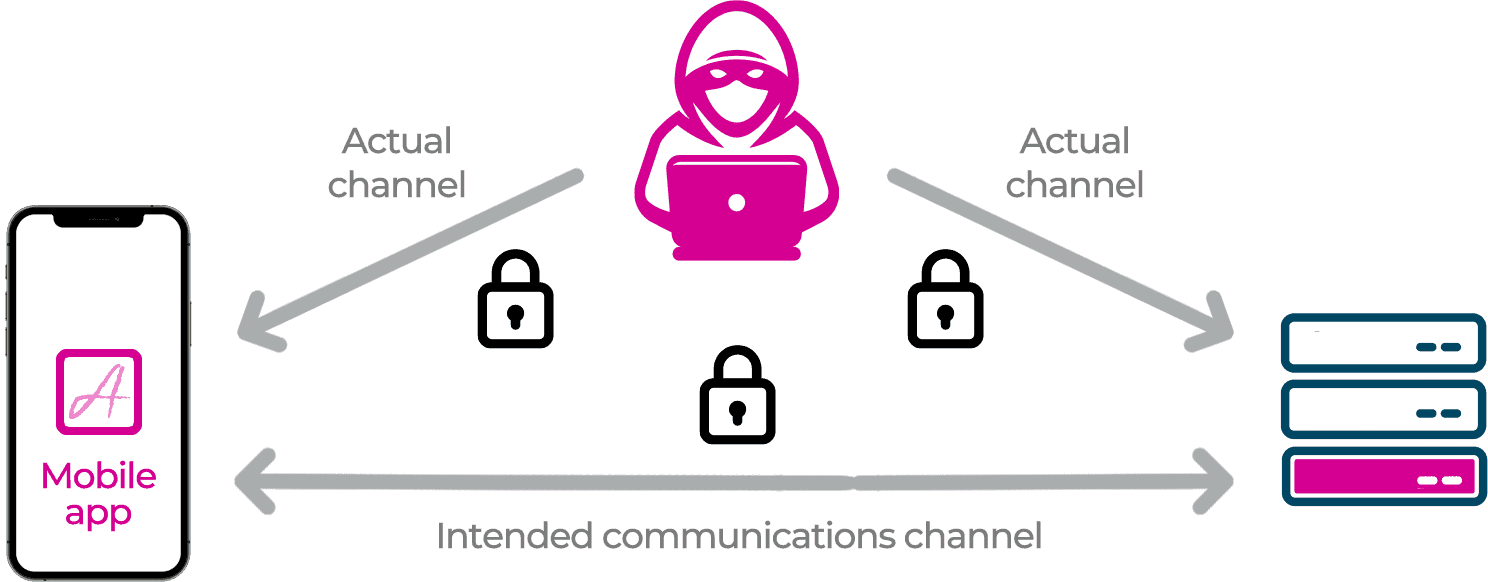
Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks
Modern apps communicate using a secure TLS connection between the app and the backend APIs. A common mistake is to believe that this encryption makes sure that the data is not vulnerable to eavesdropping by a Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attacker. Although TLS ensures that the data is encrypted end-to-end, it can’t be certain that one of the ends is actually your app.
It is possible to trick the app into allowing communication indirectly via an MitM attacker that can observe and potentially modify all of the traffic. Such MitM approaches are commonly used by attackers to reverse engineer an API protocol and extract secrets and API keys for subsequent attack.
How can You Prevent MitM Attacks?
See why MitM attacks are a particular issue for mobile apps, and understand the techniques used by hackers. See how certificate pinning can help thwart mobile MitM attacks and how dynamic pinning can streamline mobile app devops.
Download the white paper today to understand the MitM threat to mobile apps and the steps you must take to enhance your security and protect your organization’s data and revenue from being hacked.
MitM Webinar
This webinar recording shows why MitM attacks are a particular issue for mobile apps, providing an in-depth analysis of the problem and the techniques used by hackers - and how to stop them.

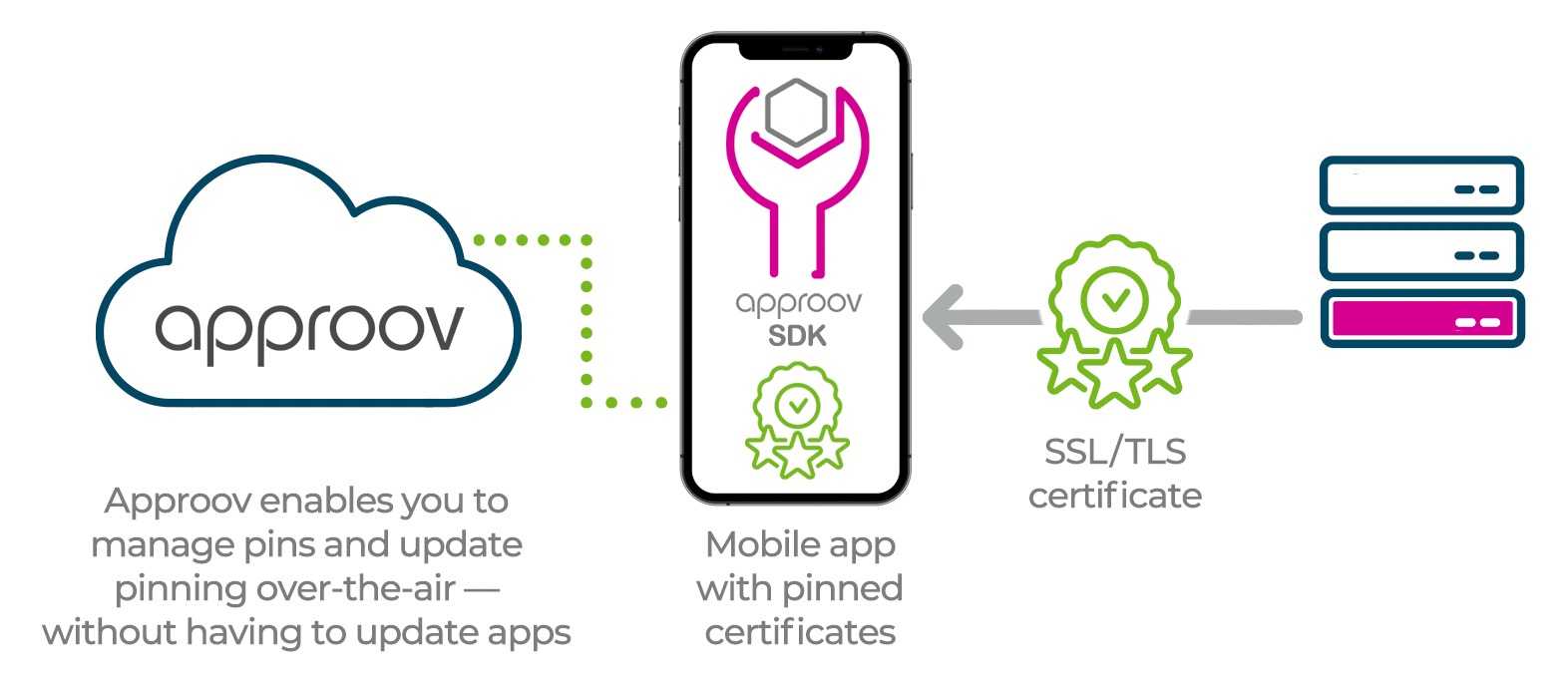
Certificate Pinning Simplified and Secure
Approov provides support for updating pins dynamically over-the-air with no need to update the app. Certificate rotations can be handled instantly and cleanly, with no risk of interruption to customer service. Our frontend Quickstarts implement dynamic pinning across a wide range of different development frameworks.
When it is not possible to perform a Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attack by subverting the trusted certificates on a device, attackers turn to other techniques. Sometimes referred to as “Man-in-the-App” attacks, function-hooking frameworks (such as Frida) are used to nullify pinning implementations so that attacker certificates are accepted. Since Approov detects hooking frameworks, valid Approov tokens or Runtime Secrets are never issued in such cases, stopping attacks because the backend APIs will not respond.

